Virtual Analysis of Segmental Bimaxillary Surgery: A Validation Study
Authors
Holte MB, Diaconu A, Ingerslev J, Thorn JJ & Pinholt EM

Abstract
Purpose: Three-dimensional (3D) assessment of orthognathic surgery is often time consuming, relies on manual re-identification of anatomical landmarks or is limited to non-segmental osteotomies. The purpose of the present study was to propose and validate a semi-automatic approach for 3D assessment of the accuracy and postoperative outcome of segmental bimaxillary surgery.
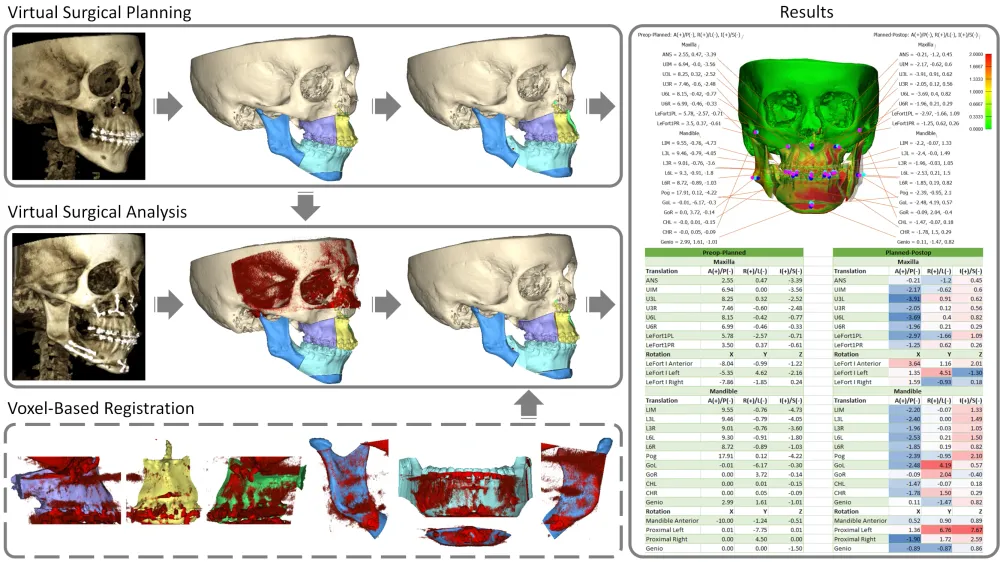
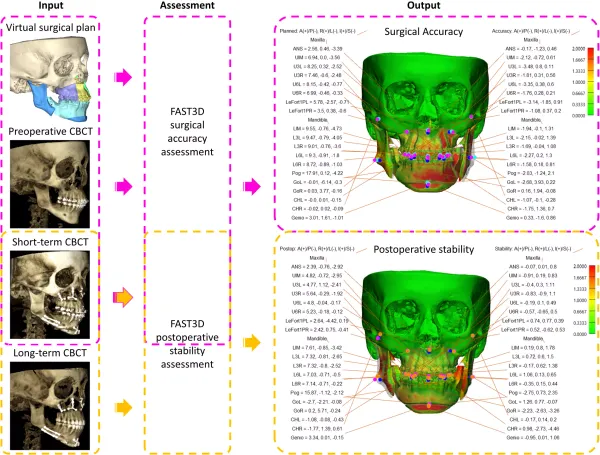
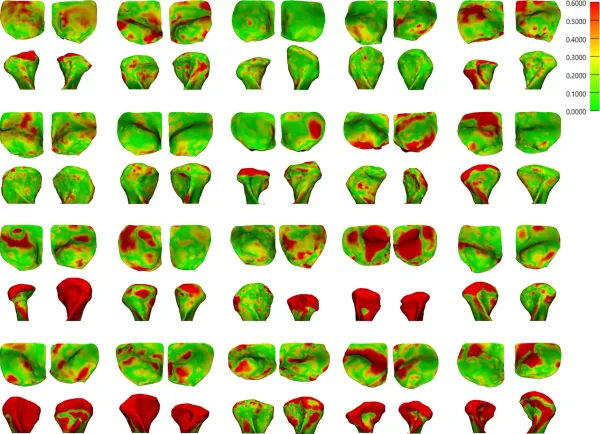
Methods: A semi-automatic approach was developed and validated for virtual surgical analysis (VSA) of segmental bimaxillary surgery using a pair of pre- and postoperative (two weeks) cone-beam computerized tomography (CBCT) scans. The output of the VSA, the accuracy of the surgical outcome, was calculated as 3D translational and rotational differences between the planned and postoperative movements of the individual bone segments. To evaluate the reliability of the proposed VSA, intra-class correlation coefficients (ICC) were calculated at a 95% confidence interval on measurements of two observers. The VSA was deemed reliable if the ICC was excellent (> 0.80) and the absolute difference of the repeated intra- and inter-observer translational and rotational measurements were significantly lower (p < .05) than a hypothesized clinical relevant threshold of one voxel (0.45 mm) and one degree, respectively.
Results: A total of ten subjects (six male; four female; mean age 24.4 years) with skeletal class II and III, who underwent segmental bimaxillary surgery, comprising a combined three-piece Le Fort I-, bilateral sagittal split osteotomy incl. genioplasty, were recruited. The intra- and inter-observer reliability was excellent, ICC range [0.96 – 1.00]. The range of the mean absolute difference of the repeated intra- and inter-observer translational and rotational measurements were [0.07 mm (0.05) – 0.20 mm (0.19)] and [0.11˚ (0.08) – 0.63˚ (0.42)], respectively. This was significantly lower than the hypothesized clinical relevant thresholds (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: The validation showed that the VSA has excellent reliability for quantitative assessment of the postoperative outcome and accuracy of segmental bimaxillary surgery.